
By University of Bristol May 17, 2025
Collected at: https://scitechdaily.com/quantum-speed-hack-extra-qubits-slash-measurement-time-without-losing-precision/
Quantum scientists have cracked a longstanding problem by devising a method to speed up measurements without losing accuracy, a key hurdle for quantum technology.
By cleverly adding extra qubits, they traded “space” for time, gathering more information faster without destabilizing the fragile quantum systems. This innovative approach, involving top researchers from several major universities, could soon become a standard tool as the race to quantum supremacy heats up.
New Breakthrough in Quantum Measurements
Researchers have discovered a new method to speed up quantum measurements — a key step toward advancing the next generation of quantum technologies.
Fast and accurate quantum measurements are essential for future quantum devices. However, quantum systems are extremely fragile; even small disturbances during measurement can cause significant errors. Until now, scientists faced a fundamental trade-off: they could either improve the accuracy of quantum measurements or make them faster, but not both at once.
Now, a team of quantum physicists, led by the University of Bristol and published in Physical Review Letters, has found a way to break this trade-off.
How Extra Qubits Make a Difference
The team’s approach involves using additional qubits, the fundamental units of information in quantum computing, to “trade space for time.” Unlike the simple binary bits in classical computers, qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously, a phenomenon known as superposition.
In quantum computing, measuring a qubit typically requires probing it for a relatively long time to achieve a high level of certainty. However, by introducing extra qubits into the measurement process, researchers can gather more information in less time, significantly accelerating the measurement without losing accuracy.
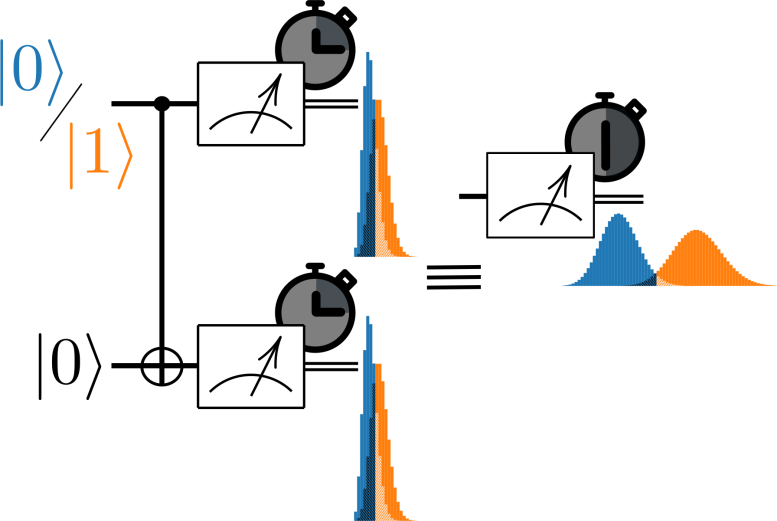
Explaining the Concept Through an Everyday Analogy
Chris Corlett, a PhD student at the University’s School of Physics, and first author on the paper, explained: “Imagine you are shown a picture of two glasses of water – one with 25ml and the other with 20ml, and you have to determine by sight which glass has more water in it. If you’re only shown the picture for one second, you might struggle to tell which glass is more full, but if you’re shown the picture for two seconds, then you can be more confident that you chose the glass with more water in it.
“In our scheme, by including an additional qubit, you increase the amount of information the probe can gather in a fixed amount of time, so we can be more confident about our answer. Adding the qubit is like doubling the volume of each glass to 50ml and 40ml, making it easier to distinguish which is more full in a shorter amount of time due to the greater difference between the two volumes.
“A significant benefit of our approach is that this relationship continues with additional qubits – so for example if you added a third qubit and, by analogy, the volume of the glasses now appears as 75ml and 60ml, you would be able to tell which was greater, with confidence, in just 0.66 seconds – this is the intuition behind our solution.”
Collaborative Discovery Across Leading Universities
Chris made the breakthrough working with his supervisors, Professor Noah Linden, Professor of Theoretical Physics, and Dr Paul Skrzypczyk, Associate Professor of Physics, along with collaborators from the University of Oxford, Strathclyde University, and Sorbonne Université in Paris.
Remarkably, the team’s process allows the quality of a measurement to be maintained, or even enhanced, even as it is sped up. The method could be applicable to a broad range of leading quantum hardware platforms. As the global race to build the highest-performance quantum technologies continues, the scheme has the potential to become a standard part of the quantum read-out process.
Reference: “Speeding Up Quantum Measurement Using Space-Time Trade-Off” by Christopher Corlett, Ieva Čepaitė, Andrew J. Daley, Cica Gustiani, Gerard Pelegrí, Jonathan D. Pritchard, Noah Linden and Paul Skrzypczyk, 27 February 2025, Physical Review Letters.
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.134.080801
I precisely needed to thank you very much yet again. I am not sure what I would have worked on in the absence of the actual concepts discussed by you concerning such area. It truly was a very terrifying issue in my opinion, but seeing the specialized fashion you solved it made me to cry over fulfillment. Now i am happier for the guidance and in addition expect you really know what a powerful job that you’re putting in teaching people using your websites. Most probably you’ve never met all of us.

Leave a Reply