
January 16, 2026 by Jeff Shepard
Collected at: https://www.eeworldonline.com/what-is-physical-artificial-intelligence-and-why-is-it-important/
Physical artificial intelligence (PAI) refers to AI systems that can perceive, understand, reason about, and interact with the physical world in real time through sensors and actuators. Unlike digital AI (DAI), which operates in virtual domains, PAI powers tangible actions in dynamic, real-world environments.
PAI is used in closed-loop systems where the AI model not only makes decisions about data but also acts on those decisions and directly interacts with its surroundings. Specialized software is one of the keys to implementing PAI.
For example, Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models are advanced AI systems that enable systems like robots to understand visual scenes (like uncut grass), interpret text commands (like “mow the lawn”), and generate precise motor control outputs required for complex real-world tasks.
PAI also uses foundation models like specialized large language models (LLMs) or small language models (SLMs) for basic reasoning. Simulation platforms like NVIDIA Omniverse are used to create realistic virtual worlds for training PAIs using synthetic data in preparation for real-world operation.
Machine learning (ML) tools are used for assembling training models and data manipulation, and analysis tools are used for cleaning, transforming, and exploring data
Finally, an action decoder, for example, a virtual motor cortex, translates the output from the PAI system into continuous, low-level movements, like joint angles and forces in a robot. All that happens in real time and in response to changing conditions in the real world. That creates specific design challenges.
PAI design considerations
PAI applications occur in real time. There’s not enough time for complex software execution or cloud connectivity. Local processing and control are a must to support millisecond decision speeds.
Sensor data can be subject to noise, hysteresis, and other sources of uncertainty. PAI systems must perform reliably with imperfect sensor data.
Actuators like motors and solenoids are inherently imperfect and don’t necessarily move precisely or repeatably. PAI feedback loops must be able to recognize and quantify actual movement, not just the anticipated “perfect” movement, and make the required adjustments in real time. Otherwise, cumulative errors can build up and result in unexpected results.
In applications like robotics or autonomous vehicles, PAI can be required to anticipate the movement of objects like people or other vehicles and make decisions based on expected near future conditions, not just the immediate environment.
Safety and reliability are mandatory. Failures can happen quickly and have real-world consequences. Physical AI systems must be tested extensively, especially when operating near or with people. In multivariable contexts, PAI systems need to prioritize tasks by urgency to perform important tasks in a timely and safe manner.
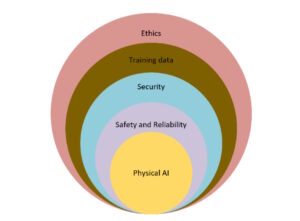
In regulated industries or safety-critical applications, designers must be able to understand and explain the AI model’s decisions. That often involves factors like ethics, sources and contents of training data, and operational security (Figure 1).
Learning to improve future performance
Continuous learning helps PAI applications adapt. It supports incremental updates to knowledge databases using new sensor data and experience with actuator performance. It’s important to prevent so-called catastrophic forgetting of existing knowledge while incorporating new data. Properly implemented, continuous learning can enable real-time adjustments and improved performance in dynamic environments.
Real-time learning loops are feedback mechanisms that enable PAI systems to continuously add new data from sensors and actuators and support immediate refinements to their understanding of the environment and resulting actions. Incremental updates to models can also make PAI systems more resilient and responsive while minimizing demands on computing resources.
ML and PAI data drift resilience is important when constructing models and systems that can detect, adapt to, and maintain performance despite changes in real-world data statistical distributions over time, preventing reductions in accuracy from changes in user behavior or trends.
Some PAI systems use modular data architectures that include specific modules for activities like data pre-processing, training, and adaptation. These architectures allow specific modules to handle factors like new sensors or faulty data without disrupting core functions.
Why PAI is important
PAI is a transformational technology moving AI from screens to physical activities, enabling fully autonomous factories and vehicles, humanoid robots, and other applications. At the same time, PAI will enable those autonomous systems to coordinate activities with human collaborators (Figure 2).

PAI moves AI from thinking and talking to performing physical tasks. For example, in the healthcare industry, PAI will enable personalized monitoring and treatments, advanced diagnostics, and improved surgical precision.
Summary
PAI moves AI from chatbots into robots and enables real-time interaction with the physical environment. Among the key applications for PAI will be a wide array of robots for industrial, medical, consumer, and other applications, as well as autonomous vehicles. PAI is here and is a rapidly expanding technology.
References
AI and humanoid robots, Mercedes-Benz
Embracing the Rise of Physical AI: Are We Ready for the Robot Era?, Bonsystems
Physical AI: Bridging the Gap Between AI and the Real World, Techvify
Physical AI is changing manufacturing, World Economic Forum
Physical AI: The Intelligence Behind Smarter Spaces, Kloudspot
Transforming the physical world with AI: the next frontier in intelligent automation, AWS
What is Physical AI, HPE
What is Physical AI?, Iris
What is Physical AI?, NVIDIA
What is Physical AI, and why Edge Computing makes it Possible?, Premio

Leave a Reply