October 9, 2025 by Jeff Shepard
Collected at: https://www.eeworldonline.com/are-there-any-benefits-from-generative-ai-hallucinations/
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) hallucinations, where an AI delivers incorrect or fabricated information, can offer benefits, especially in creative and exploratory domains like drug discovery.
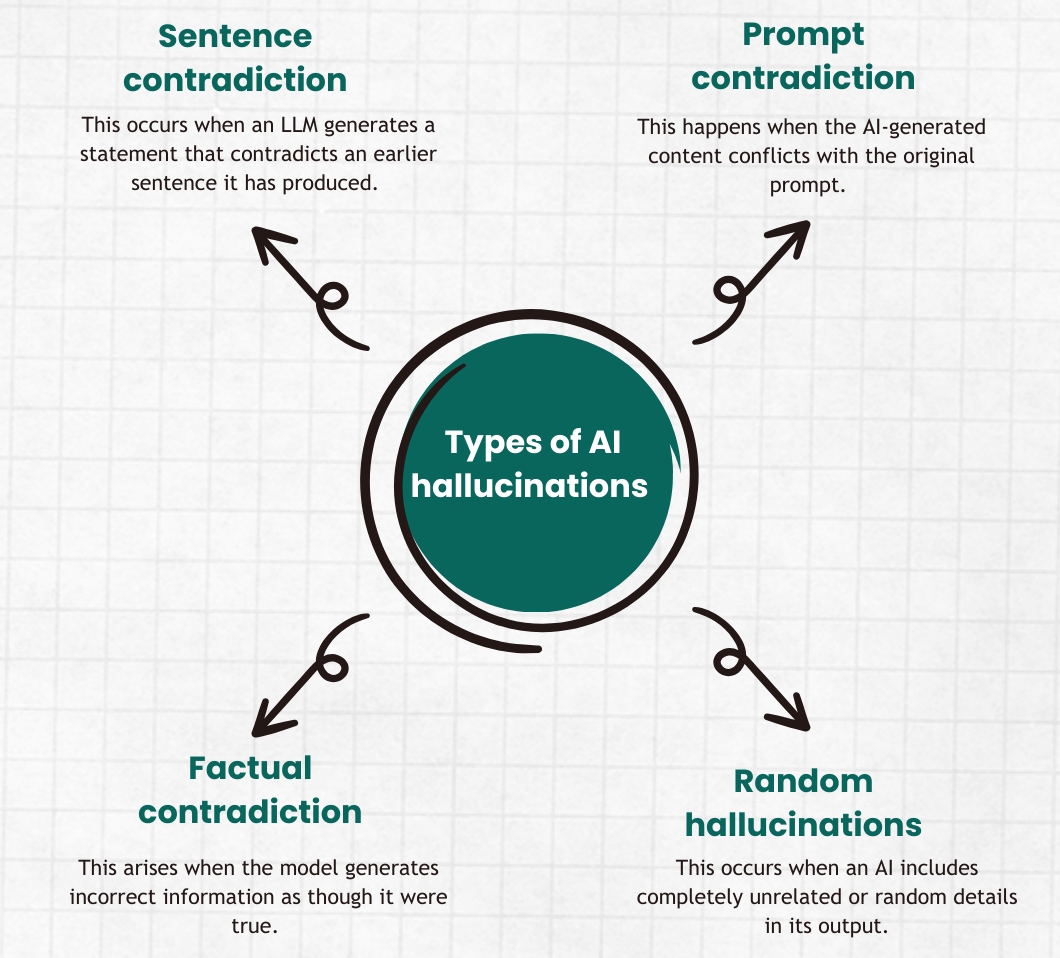
There are four common types of AI hallucinations (Figure 1). Not all types are equally desirable or useful.
- General contradictions include context conflicts and sentence contradictions. For example, an AI could respond to a request for a forward converter schematic by providing information on how a football forward fits into a specific playing situation.
- Prompt contradictions occur when the output disregards the input. If an AI responds with “Happy anniversary, mom and dad,” when the prompt was for a congratulatory graduation greeting for a niece.
- Factual contradictions occur when an AI model presents incorrect information as though it’s true, like “Thomas Edison invented the Internet.”
- Irrelevant or random hallucinations occur when unrelated or random details are included in the output. For example, when creating an image of a landscape, the AI adds random elements that don’t belong, such as a face appearing to float in the air.
Why does AI hallucinate?
AI hallucinations are both more and less than mistakes in the traditional sense. They are sometimes referred to as “confabulations” or “fabrications” to better reflect their nature. The term hallucination is generally meant to emphasize the unpredictable nature of LLMs and their tendency to respond to every prompt.
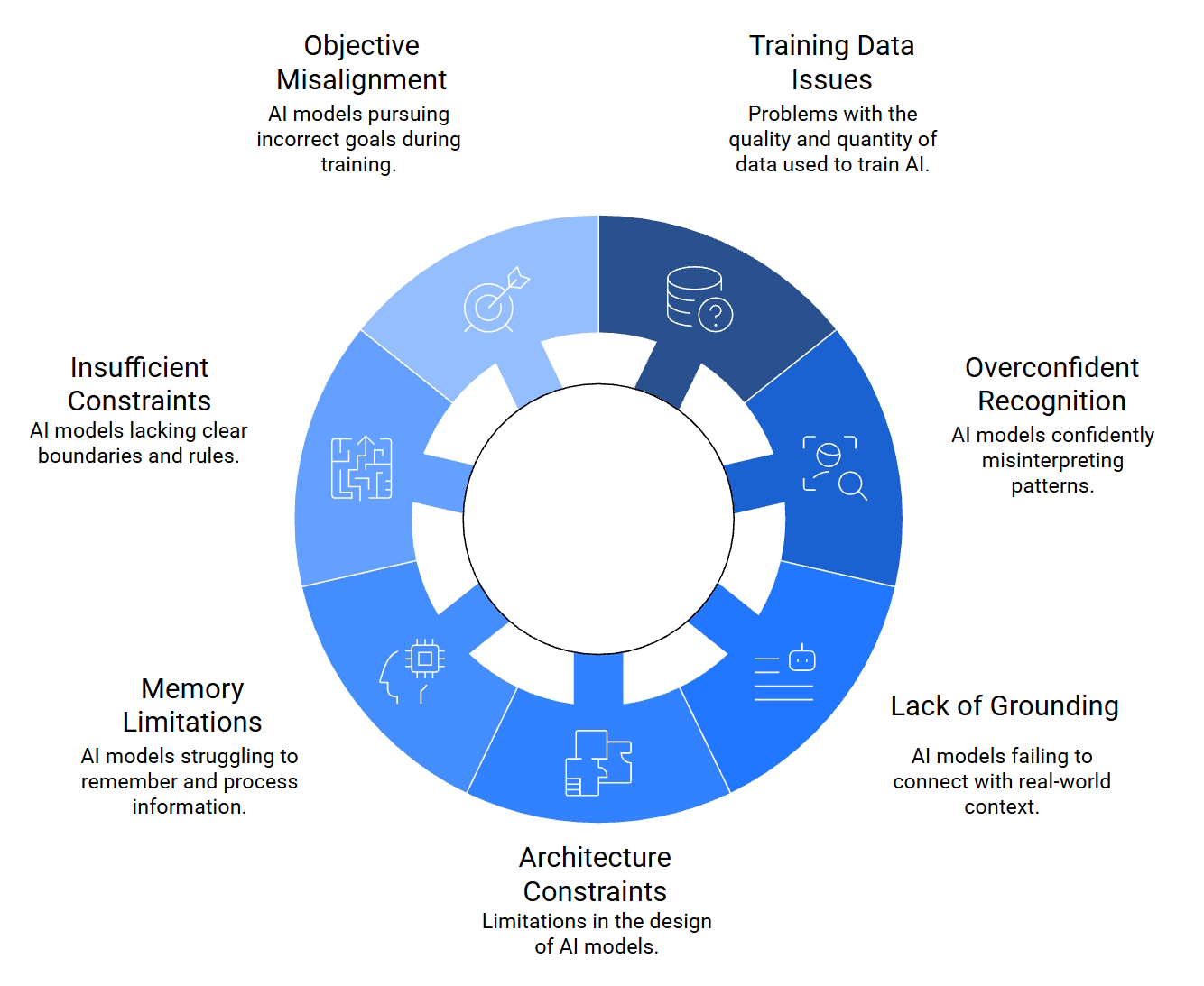
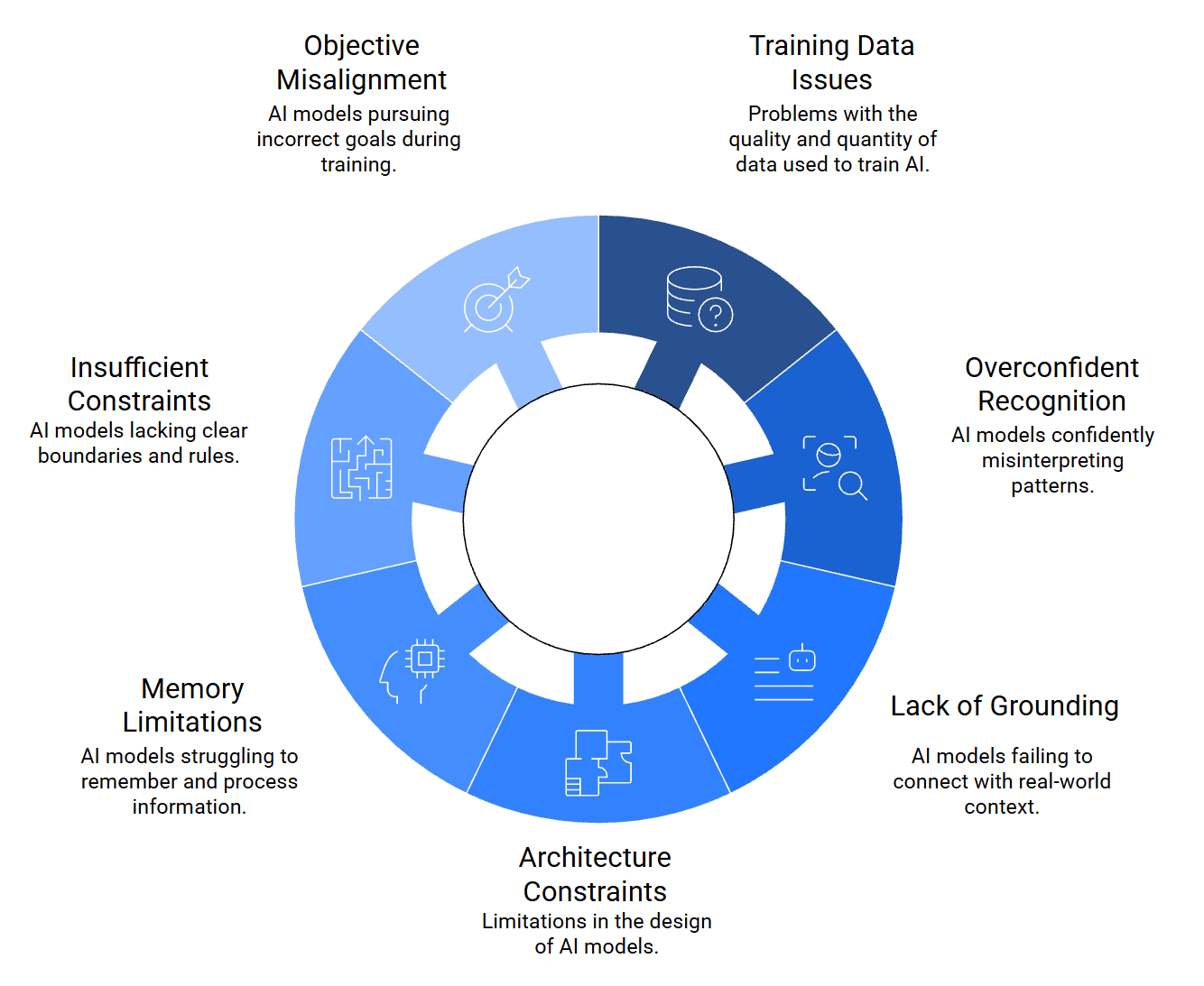
An AI is limited to its training and doesn’t know what it doesn’t know. That can apply to limitations in training techniques and training data, limitations in model designs, lack of real-world context or empathy, and numerous other factors (Figure 2).
Using RAG, TAG, and RAFT to minimize hallucinations
Retrieval augmented generation (RAG), table augmented generation (TAG), and retrieval augmented fine-tuning (RAFT) can minimize AI hallucinations by helping it respond beyond its initial training and grounding responses in verifiable, external knowledge rather than allowing it to rely solely on its potentially outdated training data. All three techniques provide the model with additional context during the response generation process.
RAG is implemented by retrieving and incorporating information from unstructured data sources like documents and web pages to improve AI responses. TAG is leveraging structured data from databases beyond the initial training database.
RAFT is designed for use in dynamic information environments. The fine-tuning in RAFT is a type of AI continuous learning where the LLM itself, not just the immediate response, is modified.
Human oversight and HITL
A human-in-the-loop (HITL) approach can be used to prevent or harness AI hallucinations. HITL integrates human expertise and judgement into the AI process. When implementing HITL, subject matter experts (SMEs) review and correct AI outputs, validate decisions, and provide continuous feedback to the model.
HITL and the integration of SMEs are particularly important for high-risk applications, where errors could have significant negative consequences. SMEs add common sense, contextual awareness, and the critical thinking that AI is incapable of providing.
HITL can also be used to ensure that scientific investigations and engineering applications using AI adhere to legal, ethical, and regulatory standards, which are vital in fields like medicine and criminal justice.
Harnessing hallucinations
In scientific investigations involving areas like drug discovery or materials development, the HITL approach works to harness AI hallucinations by deliberately provoking a model’s imaginative outputs.
For example, hallucinations can be caused by asking questions that require knowledge not in the training data, where the AI is encouraged to “be creative” beyond its factual knowledge base.
Scientists can use the provoked hallucinations to formulate new, testable hypotheses. The combination of human knowledge and intuition, plus AI’s ability to rapidly produce provoked hallucinations, can significantly speed up and expand the discovery process.
Summary
There are several sources of AI hallucinations. In most instances, hallucinations can’t be eliminated, but tools like RAG, TAG, and RAFT can help minimize the generation of hallucinations. HITL can be used to eliminate many AI hallucinations, and it can be used as part of the scientific discovery process to guide hallucinations into productive paths and speed the development of new insights.
References
3 Ways to Prevent AI Hallucinations, WillowTree
Addressing 6 challenges in generative AI for digital health, ResearchGate
AI Hallucinations: Meaning, Causes, Real Life Examples & Best Ways to Prevent LLM Hallucinations, Enkrypt AI
AI Hallucinations: What Are They? Recognizing the Risks and Solutions, HiTechNectar
AI hallucinates more frequently as it gets more advanced, Live Science
Debunking Common Misconceptions about Generative AI, Brilworks
Generative AI hallucinations: Why they occur and how to prevent them, Telus Digital
How to protect against and benefit from generative AI hallucinations, MarTech
Not All Hallucinations Are Bad: The Constraints and Benefits of Generative AI, NTT Data
Turning AI hallucinations into innovations, Reaktor
Understanding AI Hallucinations: Implications and Insights for Users, Signity
What is human-in-the-loop?, IBM

Leave a Reply