August 27, 2025 by National Taiwan University
Collected at: https://techxplore.com/news/2025-08-detector-significantly-energy-consumption-generation.html
Cell-free (CF) MIMO networks are emerging as a key B5G/6G technology for improved connectivity, spectral efficiency, and service quality. A recent study proposes a novel CF-MIMO signal detector that can reduce energy consumption by up to 58%.
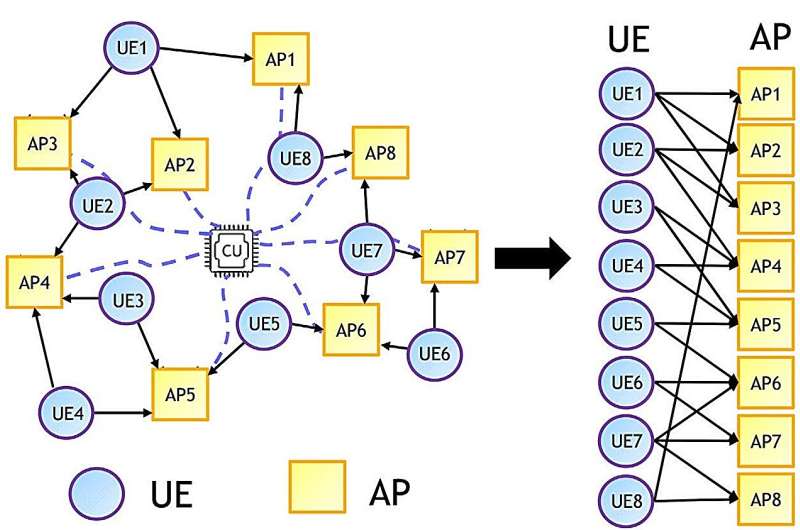
In the race toward next-generation wireless communication, researchers are exploring new technologies that can handle the growing demand for faster, more reliable, and more efficient data transmission. One of the most promising advances in this space are cell-free multiple input multiple output (CF-MIMO).
Unlike traditional systems that rely on a single base-station, cell-free MIMO employs a distributed network of smaller base-stations to serve users simultaneously. This design promises significant improvements in connectivity, spectral efficiency, and quality of service. However, fully realizing these benefits requires advanced techniques to detect data signals effectively.
To address this challenge, the authors of the study propose a new detector called DMPACT2. At its core, DMPACT2 builds on the concept of the well-known message-passing algorithm, but introduces a unique feature: the ability to dynamically adjust its underlying factor graph. In simpler terms, it learns to allocate computing resources more intelligently, focusing effort where it matters most.
To further reduce complexity, two supporting techniques are applied. These optimizations cut down computational load by as much as 99% without sacrificing accuracy. The study is published in IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications.
The results are compelling. Simulations show that DMPACT2 achieves error rates that come very close to those of the optimal detector. Even more impressively, DMPACT2 can reach the same target error rate with significantly lower signal-to-noise ratios than its competitors, making it both accurate and efficient under real-world conditions.
To provide a fairer evaluation, the researchers also introduced a new measure called power-normalized bit rate, which jointly considers throughput, error rate, computational complexity, transmission power, and backhaul traffic. Under this metric, DMPACT2 consistently outperforms other detection methods, marking it as a strong candidate for future wireless systems.
As Prof. Tzi-Dar Chiueh emphasizes, “The key to next-generation wireless is not just higher performance, but smarter use of limited resources—and that is precisely what DMPACT2 demonstrates.”
More information: Ti-Yu Chen et al, Energy-Efficient Detection Using Message Passing Algorithm With Dynamic Factor Graph for Uplink MIMO Communications in Cell-Free Networks, IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications (2025). DOI: 10.1109/TWC.2025.3550134
The very core of your writing whilst sounding reasonable originally, did not settle perfectly with me after some time. Someplace throughout the paragraphs you actually were able to make me a believer but only for a short while. I however have a problem with your jumps in logic and one would do well to fill in all those breaks. When you can accomplish that, I will definitely end up being fascinated.

Leave a Reply