December 15, 2025 by Jeff Shepard
Collected at: https://www.eeworldonline.com/why-is-maximum-data-rate-always-lower-than-bandwidth/
Bandwidth represents the theoretical maximum capacity, while the data rate (or throughput) is the actual, real-world speed that is reduced by factors like latency, protocol overhead, network congestion, and physical limitations. The distinction is important as data rates in digital systems are on a continual upward trajectory.
Data is sent using various communication protocols. These protocols have “overhead” that consumes some bandwidth but does not directly contribute to data transmission. For example, data may be structured into packets, there may be error detection and correction algorithms involved, and security functions are often implemented.
Latency can reduce data rates. Sources of latency include physical distance, network congestion, transmission medium type, and hardware limitations. Other factors are software processing, queuing delays, and the number of hops a data packet must travel. Latency can be a significant and not always controllable factor.
Network congestion can significantly slow data transmission and reduce throughput. It can result from a variety of causes, some innocent, like an excess demand for data capacity from multiple users, and some malicious, like distributed denial of service (DDOS) attacks.
Packet loss
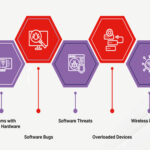
Packet loss can be a major cause of poor network performance and can severely limit effective bandwidth. Packet loss can be caused by network congestion, hardware issues, and interference. Other sources include software bugs, incorrect network configurations, and security threats. On wireless networks, interference and weak signals are common culprits, while on wired networks, faulty cables or ports are more likely sources.
When packets are lost, the network must send them again, which uses up bandwidth and slows down the connection. The retransmission process also delays communication, increasing latency. The bigger the impact on latency, the more time it takes to retransmit and resend data, further impacting performance.

Leave a Reply