December 12, 2025 by The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Collected at: https://techxplore.com/news/2025-12-efficiently-ai-judgments-real.html
A research team led by Professor Jaesik Choi of KAIST’s Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI, in collaboration with KakaoBank Corp, has developed an accelerated explanation technology that can explain the basis of an artificial intelligence (AI) model’s judgment in real-time.
They presented their work at the 34th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management.
This research achievement significantly increases the practical applicability of explainable artificial intelligence (hereinafter XAI) technology in fields requiring real-time decision-making, such as financial services, by achieving an average processing speed 8.5 times faster, and up to 11 times faster, than existing explanation algorithms for AI model predictions.
Growing need for real-time XAI
In the financial sector, a clear explanation for decisions made by AI systems is essential. Especially in services directly related to customer rights, such as loan screening and anomaly detection, regulatory demands to transparently present the basis for the AI model’s judgment are increasingly stringent.
However, conventional explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) technologies required the repeated calculation of hundreds to thousands of baselines to generate accurate explanations, resulting in massive computational costs. This was a major factor limiting the application of XAI technology in real-time service environments.
How the ABSQR framework works
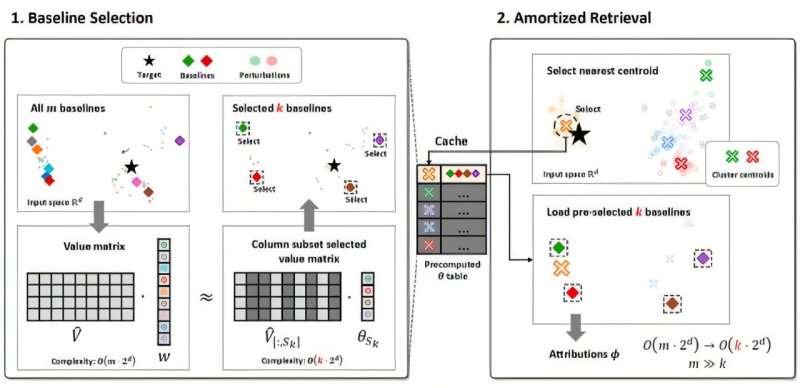
To address this issue, Professor Choi’s research team developed the ABSQR (Amortized Baseline Selection via Rank-Revealing QR) framework for accelerating explanation algorithms. ABSQR noticed that the value function matrix generated during the AI model explanation process has a low-rank structure. It introduced a method to select only a critical few baselines from the hundreds available.
This drastically reduced the computation complexity, which was previously proportional to the number of baselines, to be proportional only to the number of selected critical baselines, thereby maximizing computational efficiency while maintaining explanatory accuracy.
Specifically, ABSQR operates in two stages. The first stage systematically selects important baselines using singular value decomposition (SVD) and rank-revealing QR decomposition techniques. Unlike existing random sampling methods, this is a deterministic selection method aimed at preserving information recovery, which guarantees the accuracy of the explanation while significantly reducing computation.
The second stage introduces an amortized inference mechanism, which reuses the pre-calculated weights of the baselines through cluster-based search, allowing the system to provide an explanation for the model’s prediction result in real-time service environments without repeatedly evaluating the model.
Experimental results and industry impact
The research team verified the superiority of ABSQR through experiments on real-world datasets. Tests on standard datasets across five sectors—finance, marketing, and demographics—showed that ABSQR achieved an average processing speed 8.5 times faster than existing explanation algorithms that use all baselines, with a maximum speed improvement of over 11 times.
Furthermore, the degradation of explanatory accuracy due to speed acceleration was minimized, maintaining up to 93.5% of the explanation accuracy compared to the baseline algorithm. This level is sufficient to meet the explanation quality required in real-world applications.
A KakaoBank official stated, “We will continue relentless research and development to enhance the reliability and convenience of financial services and introduce innovative financial technologies that customers can experience.”
Chanwoo Lee and Youngjin Park, co-first authors from KAIST, explain, “This methodology solves the crucial acceleration problem for real-time application in the financial sector, proving that it is possible to provide users with the reasons behind a learning model’s decision in real-time.”
“This research provides new insights into what constitutes unnecessary computation and the selection of important baselines in explanation algorithms, practically contributing to the improvement of explanation technology efficiency.”
More information: Chanwoo Lee et al, Amortized Baseline Selection via Rank-Revealing QR for Efficient Model Explanation, Proceedings of the 34th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (2025). DOI: 10.1145/3746252.3761036

Leave a Reply