December 3, 2025 by Patricia DeLacey, University of Michigan College of Engineering
Collected at: https://techxplore.com/news/2025-12-source-framework-enables-addition-ai.html
Developers can now integrate large language models directly into their existing software using a single line of code, with no manual prompt engineering required. The open-source framework, known as byLLM, automatically generates context-aware prompts based on the meaning and structure of the program, helping developers avoid hand-crafting detailed prompts, according to a conference paper presented at the SPLASH conference in Singapore in October 2025 and published in the Proceedings of the ACM on Programming Languages.
“This work was motivated by watching developers spend an enormous amount of time and effort trying to integrate AI models into applications,” said Jason Mars, an associate professor of computer science and engineering at U-M and co-corresponding author of the study.
Challenges of integrating AI models
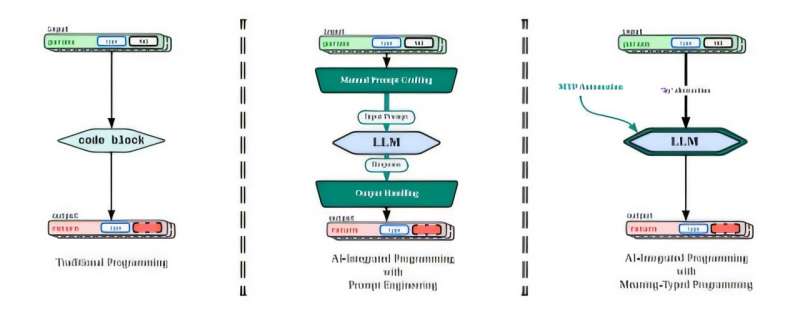
Integrating AI applications creates headaches as developers must act as translators between different operating assumptions. Conventional programming performs operations on explicitly defined variables while LLMs process natural language text as input. To make them work together, developers must manually construct textual input in a process known as prompt engineering, which can be tedious, complex and imprecise.
The new language construct, byLLM, and a supporting runtime automate prompt engineering, allowing developers to write a few lines of code instead of hundreds when integrating LLMs into real-world applications.
“This innovation makes integrating powerful AI models into software as easy as calling a function, so developers can focus on building creative solutions rather than wrestling with prompt engineering,” said Lingjia Tang, an associate professor of computer science and engineering at U-M and co-corresponding author of the study.
How byLLM bridges programming and AI
The operator “by” acts as a bridge between conventional and LLM operations. A compiler based on the meaning-typed intermediate representation gathers semantic information about the program and the programmer’s aims. An automatic runtime engine converts that semantic information into a focused set of prompts to direct LLM processing.
An evaluation showed that the byLLM method achieved higher accuracy, better runtime performance, and greater robustness compared to previous prompt engineering frameworks like DSPy. A user study evaluating byLLM’s effectiveness found that developers using byLLM completed tasks over three times faster and wrote 45% fewer lines of code.
“By inferring the programmer’s intent from code snippets, byLLM lowers the barrier for AI-enhanced programming and could enable an entirely new wave of accessible, AI-driven applications,” said Krisztian Flautner, a professor of engineering practice at U-M and co-corresponding author of the study.
The team made byLLM open source, and it has seen rapid adoption with over 14,000 downloads in one month and interest from industry partners. The open source accessibility could empower smaller teams or even non-expert programmers to create advanced AI applications, potentially opening the door to new innovations in personalized software, research tools and interactive learning environments.
Companies in finance, customer support, health care, education, and many other fields can use this approach to quickly integrate LLMs into their products with significantly reduced engineering overhead.
More information: Jayanaka L. Dantanarayana et al, MTP: A Meaning-Typed Language Abstraction for AI-Integrated Programming, Proceedings of the ACM on Programming Languages (2025). DOI: 10.1145/3763092. On arXiv: DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2405.08965
On GitHub: github.com/jaseci-labs/jaseci/tree/main/jac-byllm
Journal information: arXiv

Leave a Reply